

The Six Sigma project has not significantly improved the failure rate.

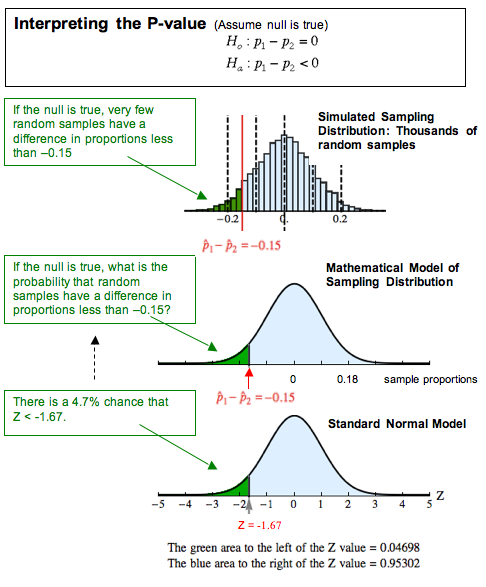
Since -0.69 is bigger than -1.96, we have to accept the null hypothesis that the population proportions are the same. An Alpha risk of 5 percent (or 0.05) corresponds to a critical value of +/-1.96 for a two-tailed test. In this case, the sample size is large enough to assume that the Z distribution follows the standardized and normally distributed z distribution. The Z-value of -0.69 is compared with the critical value that must be exceeded to reject the null hypothesis with an alpha risk of 5 percent and can be derived from the Z distribution. Using these results the Z-value is calculated as: Where p1 and p2 are the sample proportion use the sample proportions to estimate the standard error because the population proportions are unknown.

Is the standard error (SE) of the difference between the two proportions. Where (p1 – p2) is the observed difference between the sample proportions, (P1 – P2) is the difference between the population proportions assuming that Ho is true (in this example (P1 – P2) = 0). Handpicked Content: Understanding the Uses for Mood's Median Test For large sample sizes, this Z-value follows the same normal distribution as the well-known standardized z-value for normally distributed data. The test statistics of the two-proportions test is the Z- value. The alpha level is set at 5 percent (i.e., a = 0.05) In our example, the null hypothesis (Ho) and the alternative hypothesis (Ha) are: It only works, however, when the raw data behind the percentages (100 rejects out of 10,000 parts produced and 72 out of 8,000 respectively) is available since the sample size is a determining factor of the test statistics. As the name suggests it is used when comparing the percentages of two groups. The appropriate hypothesis test for this question is the two-proportions test. Did the process improve? The Two-Proportions Test In April, the process produced 8,000 widgets and experienced a total of 72 rejects (failure = 0.009, success = 0.991). A Six Sigma project was deployed to fix this problem and by March the improvement plan was in place. Consider a production process that produced 10,000 widgets in January and experienced a total of 100 rejected widgets after a quality control inspection (i.e., failure rate = 0.01, success rate = 0.99).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
